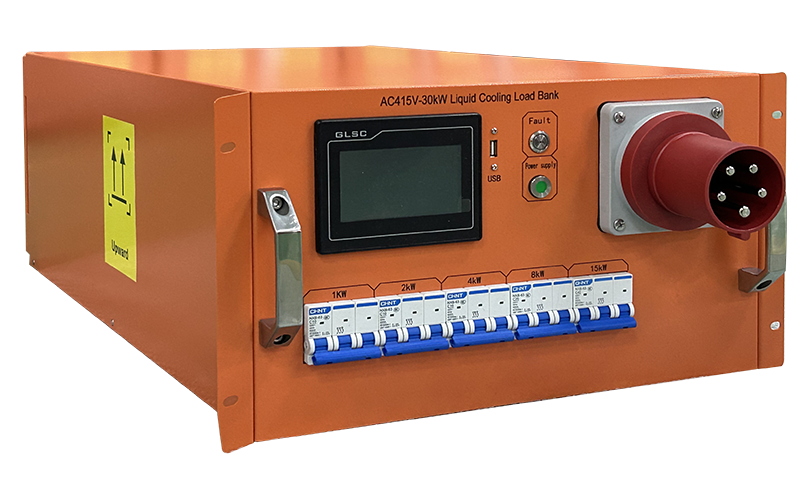
What are the essential preparations required prior to initiating a simulated test room operation using a load bank?
Time:2025-08-29
Load bank simulation testing involves strong current operation, equipment coordination and environmental regulation. If operated improperly, it is easy to cause equipment damage, safety accidents or distortion of test data. Therefore, the following aspects need to be given special attention to comprehensively cover the process monitoring before testing. Plan formulation: Clearly define the testing objectives, procedures and emergency response plans.
A scientific test plan serves as the "action guide" for load bank simulation testing. It is necessary to balance test accuracy and operational safety, clearly defining the test scope, steps, monitoring indicators, and emergency measures. Firstly, it is necessary to define the test objectives and scope. Based on the test scenarios in the computer room (such as the acceptance of new computer rooms, UPS battery life detection, and generator load capacity testing), the core test contents should be determined: For instance, when accepting newly-built computer rooms, it is necessary to focus on testing the power supply stability of the "UPS - distribution cabinet - load" circuit, as well as the start-up response time and load switching capability of diesel generators. During the operation and maintenance stage testing, attention should be paid to indicators such as the temperature rise of the equipment and the voltage fluctuation range under full load. At the same time, clearly define the test scope, mark the equipment that needs to be connected to the load bank (such as the output end of the UPS, the emergency power supply end of the generator), the test area (such as the distribution room of the computer room, the generator room), and the equipment that is prohibited from operation (such as the core business server in operation), to avoid misoperation affecting the normal operation of the computer room. Secondly, a detailed test process needs to be designed, following the logical planning steps of "no-load debugging → gradual loading → full-load operation → load unloading", clearly defining the load capacity, duration, and monitoring nodes for each stage: For instance, when testing the load-carrying capacity of a diesel generator, the process can be designed as follows: "Start the generator under no-load conditions and run it for 10 minutes to preheat → run each step at 10% of the rated load for 15 minutes and record the voltage and frequency data → increase to 100% full load and run continuously for 30 minutes. Observe the changes in the generator's rotational speed, water temperature and oil pressure → gradually unload to no-load and shut down the generator. Finally, it is necessary to formulate a complete emergency response plan, predict the possible risks during the test (such as overload tripping of the load bank, short circuit of the distribution cabinet, and generator shutdown), and clarify the emergency response procedures: for example, if an abnormal surge in the current of the load bank is found during the test, the power supply of the load bank should be immediately cut off, and check whether the wiring of the distribution cabinet is loose. If the generator gives an alarm for excessively high water temperature, the loading should be suspended, the cooling system activated, and an emergency shutdown necessary. At the same time, emergency tools (such as insulating gloves, multimeters, and fire extinguishers) and liaison mechanisms (clearly defining the contact information of the test supervisor, electrician, and technical support from the equipment manufacturer) should be provided to ensure a rapid response in case of emergencies.
News Recommendation
-
 2024-09-11
2024-09-11TRIUMPH LOAD EXHIBITING AT Enlit Europe 2024 -BOOTH 7.H08
-
 2023-04-21
2023-04-21TRIUMPH LOAD EXHIBITING AT DATA CENTER WORLD GERMANY 2023-BOOTH F909
-
 2023-04-06
2023-04-06TRIUMPH LOAD EXHIBITING AT ELECTRIC POWER TECH KOREA 2023 – Booth G109
-
 2022-05-05
2022-05-05What is the role of ac load bank for power supply?
-
 2022-05-05
2022-05-05What is the role of the load bank?